NASA’s Curiosity rover has reached an vital milestone: the robotic celebrates the tenth anniversary of its touchdown on Mars on August 5, 2012.
Over the last decade, the rover has considerably superior our understanding of the Crimson Planet by its exploration and analysis. Curiositythe primary goal of the mission was to find out whether or not or not March was as soon as liveable. In earlier missions, scientists had already decided that water was as soon as current on Mars and, actually, is at the moment current on Mars within the type of ice. However water alone isn’t sufficient to maintain life.
“To find out habitability, it’s important to know if there have been issues like natural molecules – carbon-containing molecules that life wants – sources of vitality, different molecules that life wants, like nitrogen, phosphorus, oxygen,” Curiosity undertaking assistant scientist Abigail Fraeman, who can also be a planetary scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, informed Area.com. “And we discovered all of these have been there.”
Associated: Have a good time 10 years of NASA’s Curiosity rover with these unbelievable pictures (gallery)
With the intention to discover these key habitability signatures on Mars, Curiosity takes with it instruments for drilling the planet’s floor and spectrometers just like the Pattern Evaluation at Mars (SAM) and Chemistry and Mineralogy (Chemin) that may analyze ensuing samples. In the course of the rover’s first years on the planet, it had already found the important thing necessities of life.
“So we discovered, first, that Mars was liveable, and second, that these liveable environments continued for tens of hundreds of thousands of years, very seemingly, possibly even a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of years, which was shocking and thrilling,” Fraeman stated.
The rover’s analysis of Mars rock and soil has additionally supplied new insights into groundwater cycles on Mars. “All of the rocks we have now handed by present not solely the signature of water once they have been initially deposited, however this later superimposition of 1 or two or dozens of cycles of groundwater flowing by the rocks,” stated Fraeman. “And so it actually highlighted the significance of groundwater on Mars, which might have been a very vital course of.”
However in a decade of exploration, Curiosity has found far more than the constructing blocks of life. “One of many sorts of science that does not get talked about loads, however is de facto vital and actually fascinating is the environmental science that we do,” Fraeman stated.
Curiosity has radiation detectors and environmental and atmospheric sensors which were put to good use on Mars. For instance, all through its wanderings, when Curiosity approached geological formations reminiscent of cliffs and buttes, the rover’s devices detected that the rocks blocked radiation from reaching it. “We will now use it for fashions of future astronauts. For instance, can you employ pure terrain as a defend?” Fraeman stated.
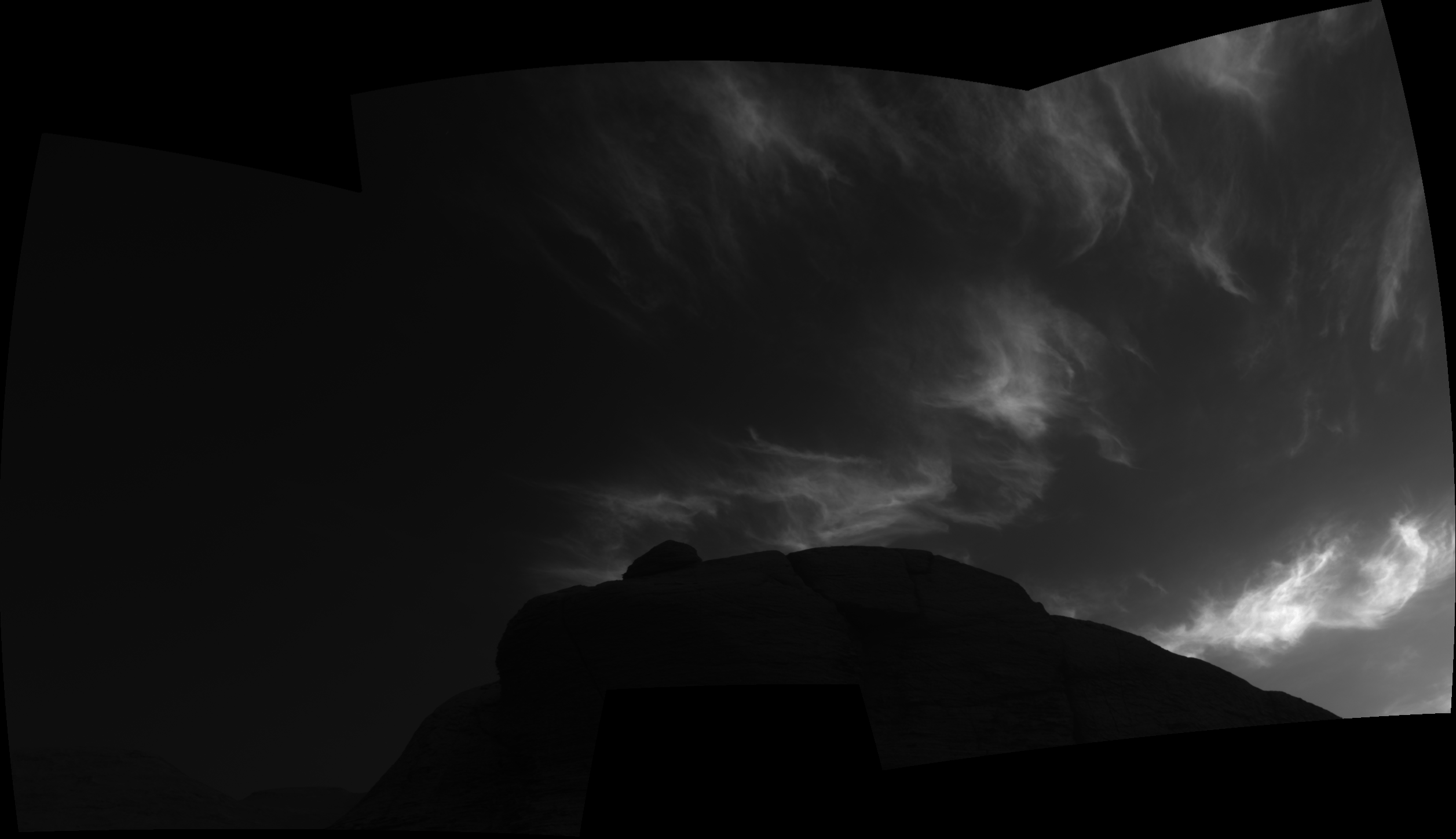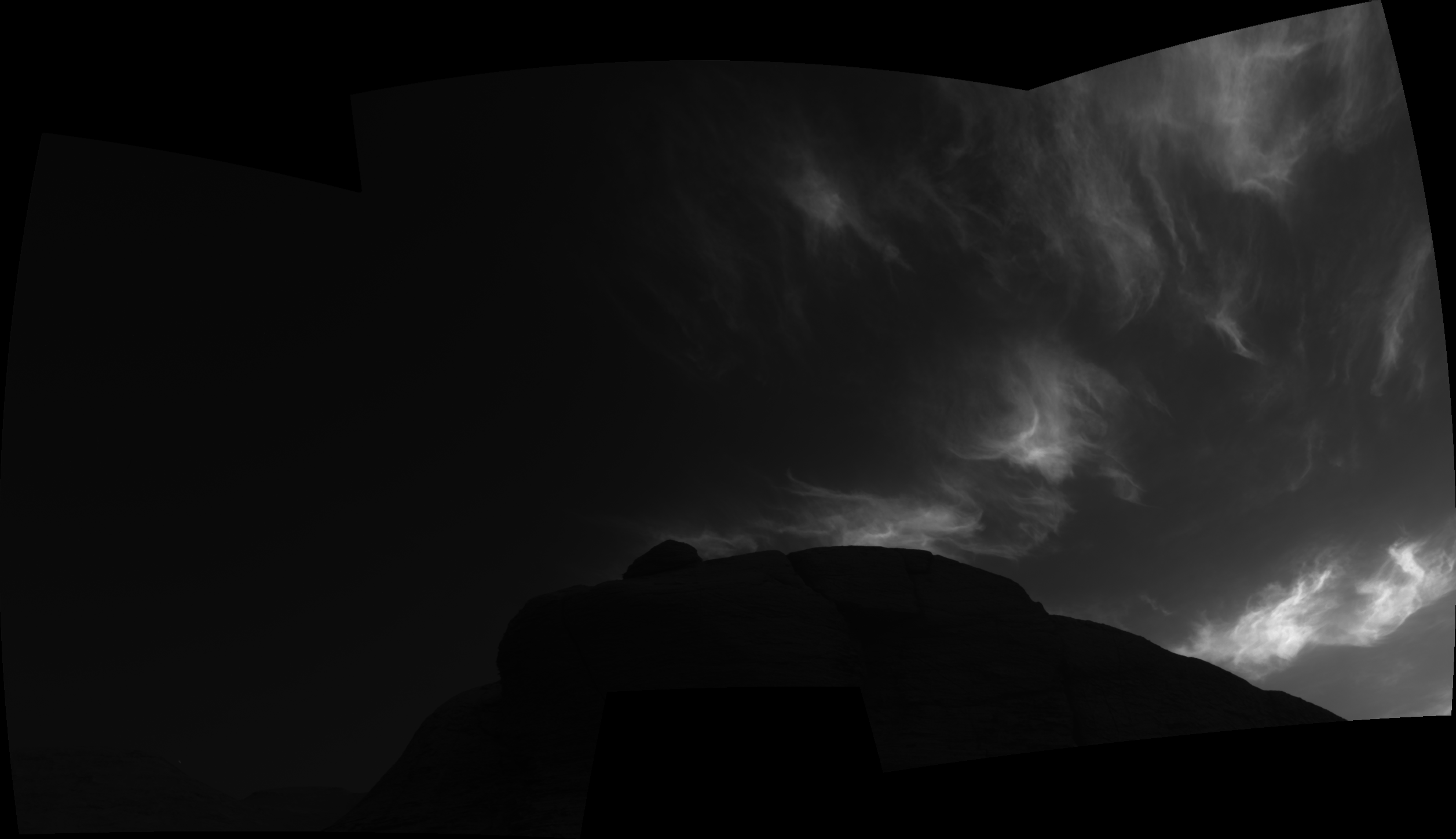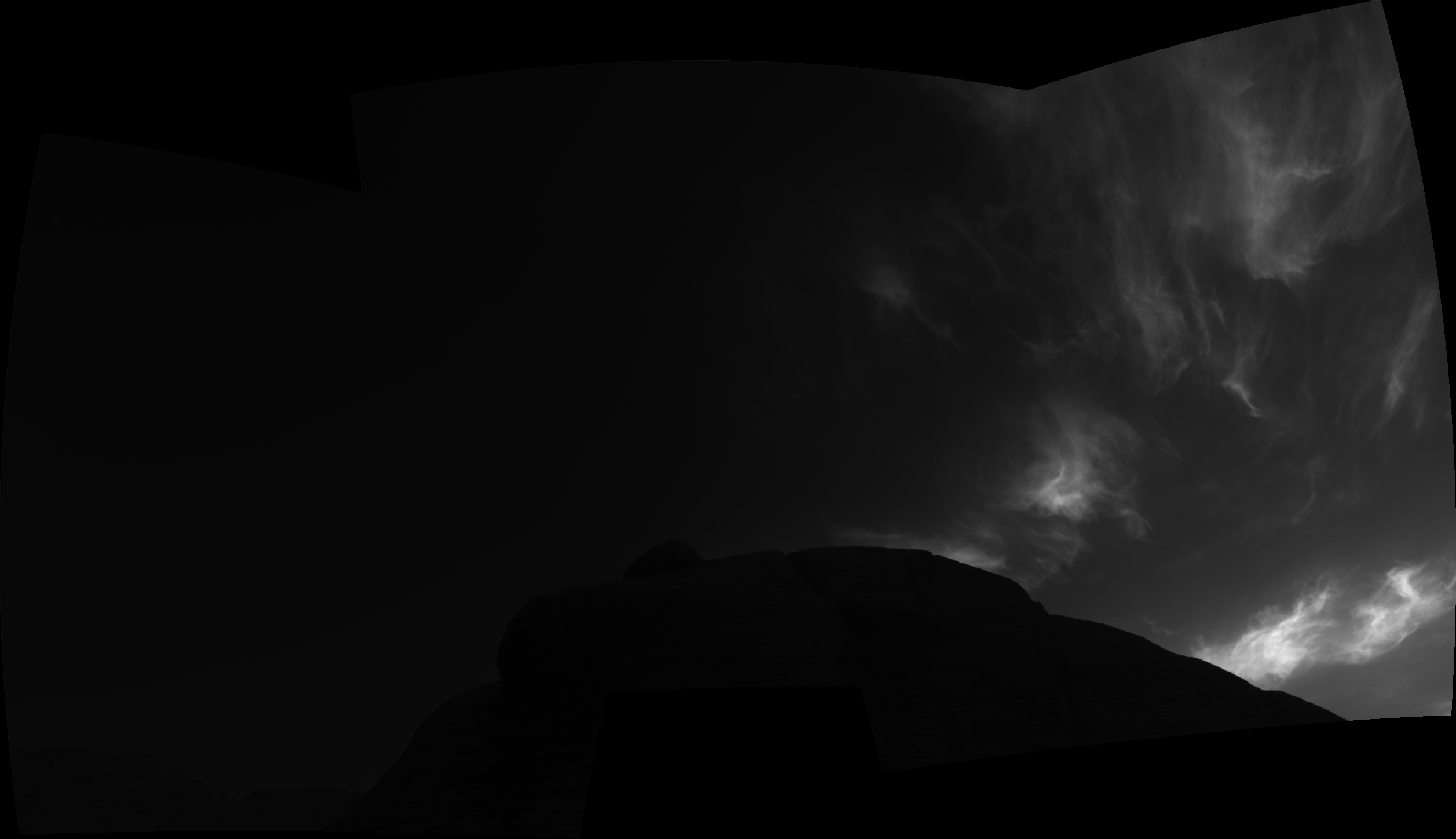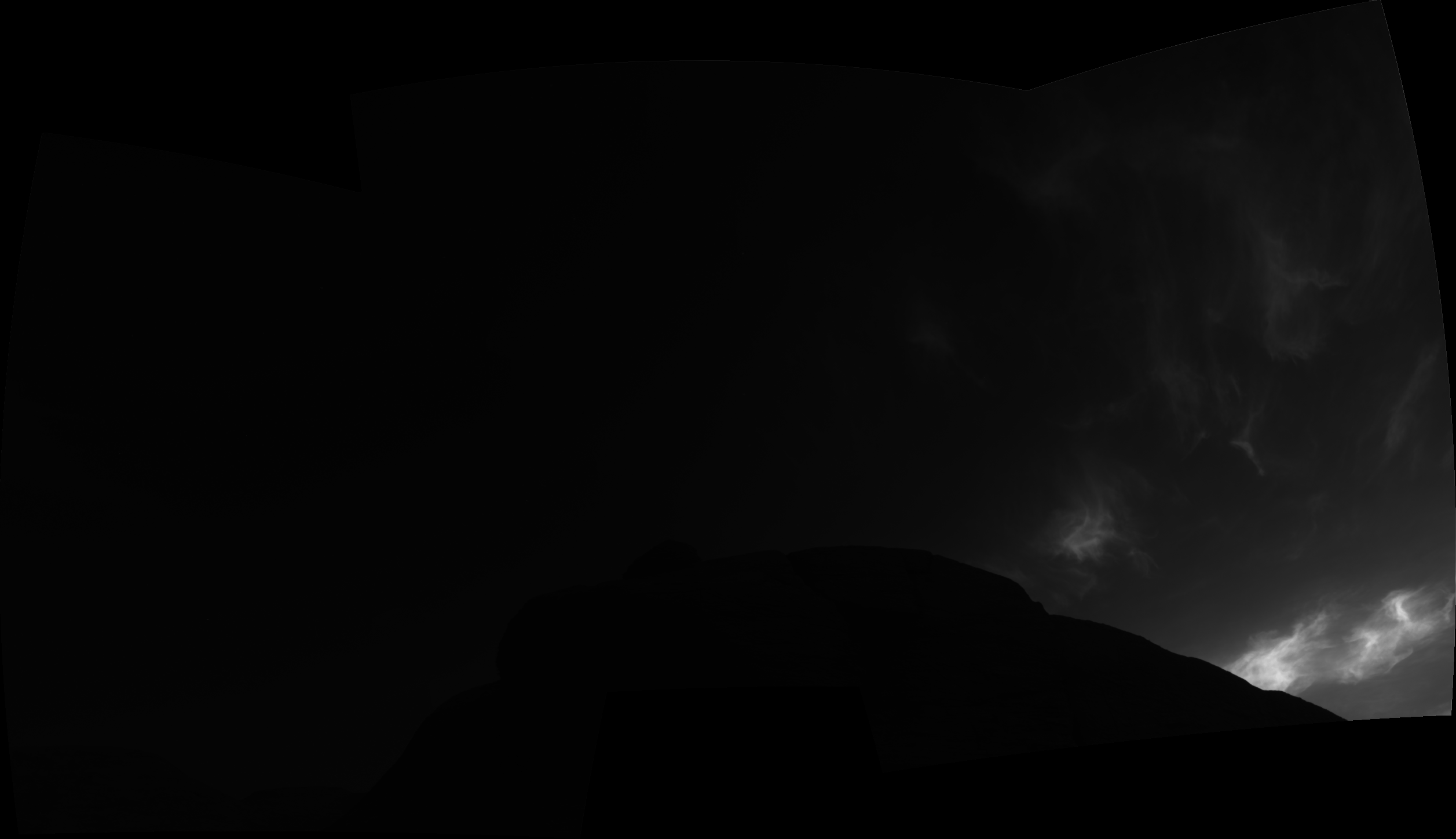
She can also be captivated by Curiosity’s examine of Martian climate, noting that final yr Curiosity photographed stunning clouds generally known as night time cloudswhich seem at sundown in winter.
Though Curiosity’s unique mission timeline lasted slightly below two Earth years, a decade later the rover continues to be in comparatively good well being – ok to proceed its work. “We’ve a little bit of arthritis, a little bit of joint ache,” Fraeman stated. Its wheels, for instance, have developed loads of holes after roughly 17.5 miles (28 kilometers) of journey with an elevation acquire of two,000 toes (600 meters). However Fraeman famous that the wheels have been accumulating injury at a comparatively sluggish charge, permitting Curiosity to maintain transferring.
“I believe what’s most outstanding to me is that every one the science devices are principally working in addition to they did after we landed,” she stated. “We’re nonetheless in a position to do the identical high quality and breadth of science as 10 years in the past, and that is fairly superb.”
The following step for Curiosity is an investigation into what occurred to Mars’ as soon as liveable local weather and the way lengthy the area remained liveable when the water started to dry up. Whereas the rover has spent the previous decade exploring lake environments — most not too long ago, an space the place sand dunes fashioned when lakes disappeared — the workforce is now sending the explorer even greater up Mount Sharp.
“We’re so near hitting what we name the Layered-Sulfate Unit, which is a very totally different a part of Mount Sharp,” Fraeman stated. “We see from orbit that it has a distinct texture, a distinct mineralogy, and we predict that is going to signify a really totally different environmental climate on Mars. We’re excited to see precisely what that environmental change was, how it’s mirrored within the rock document, and what meaning for livability.”
However earlier than Curiosity will get to all that, the workforce goes to spend a while celebrating the anniversary. “These of us who’re native to Pasadena, we will have a celebration. We will purchase Thai meals, we will have a raffle,” Fraeman stated. “I believe it’s going to simply be a joyful event to have fun accomplishments and hopefully sit up for extra enjoyable science.”
Observe Stefanie Waldek on Twitter @StefanieWaldek. Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Fb.
#Curiosity #rover #exploring #Mars #years #Heres #discovered