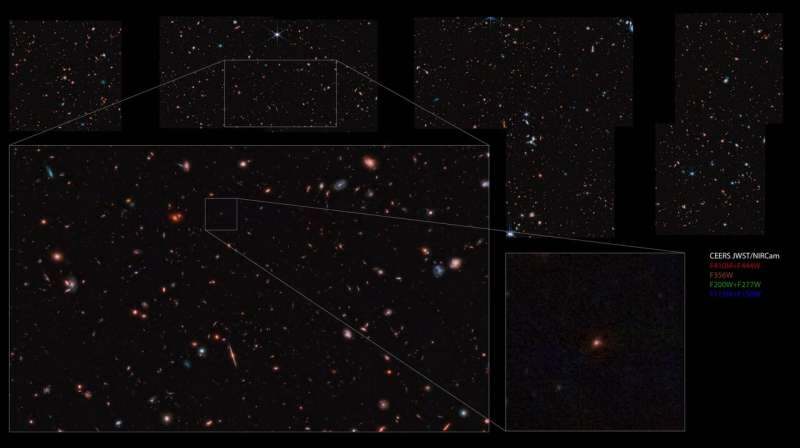
CEERS collaboration scientists have recognized an object – dubbed the Maisie Galaxy after challenge chief Steven Finkelstein’s daughter – that could be one of many earliest galaxies ever noticed. If its estimated redshift of 14 is confirmed by future observations, that might imply we see it because it was simply 290 million years after the Large Bang. Credit score: NASA/STScI/CEERS/TACC/S. Finkelstein/M. Bagley/Z. Levay.
Two new photographs from NASA’s James Webb House Telescope present what could also be one of many first galaxies ever noticed. Each photographs embody objects from over 13 billion years in the past, and one affords a a lot wider discipline of view than Webb’s first Deep Subject picture, which was launched to a lot fanfare on July 12. . The pictures signify among the first in a serious collaboration of astronomers and different educational researchers teaming up with NASA and world companions to uncover new details about the universe.
The group have recognized a very thrilling object – dubbed the Maisie Galaxy after challenge chief Steven Finkelstein’s daughter – which they imagine was noticed as a result of it was simply 290 million years after the Large Bang ( astronomers name this a redshift of z=14).
The consequence has been revealed on the pre-release server arXiv and is awaiting publication in a peer-reviewed journal. If the invention is confirmed, it will be one of many earliest galaxies ever noticed, and its presence would point out that galaxies started to kind a lot sooner than many astronomers thought.
The razor-sharp photographs reveal a flurry of advanced galaxies evolving over time – some elegantly mature pinwheels, some toddler blobby, nonetheless others wispy swirls of do-so-doing neighbors. The pictures, which took round 24 hours to gather, come from a patch of sky close to the deal with of the Large Dipper, a constellation formally named Ursa Main. This similar space of sky has beforehand been noticed by the Hubble House Telescope, as seen within the Prolonged Groth Band.
“It is wonderful to see a brilliant spot from Hubble rework into a whole, fantastically shaped galaxy in these new photographs from James Webb, and extra galaxies popping up out of nowhere,” mentioned Finkelstein, affiliate professor of astronomy on the College of Texas at Austin and the principal investigator of the Cosmic Evolution Early Launch Science Survey (CEERS), from which these photographs had been taken.
The CEERS collaboration is made up of 18 co-investigators from 12 establishments and greater than 100 collaborators from the USA and 9 different nations. CEERS researchers examine how among the first galaxies shaped when the universe was lower than 5% of its present age, throughout a interval often known as reionization.
Earlier than the precise telescope information arrived, Micaela Bagley, a postdoctoral researcher at UT Austin and one in all CEERS’ imaging leads, created simulated photographs to assist the group develop processing strategies and evaluation of latest photographs. Bagley led a stay picture processing group in order that the info could possibly be analyzed by the entire group.
The large picture is a mosaic of 690 particular person photographs that took about 24 hours to gather utilizing the telescope’s fundamental imager, known as the Close to Infrared Digital camera (NIRCam). This new picture covers an space of sky about eight instances bigger than Webb’s first Deep Subject picture, though it isn’t as deep. The researchers used supercomputers on the Texas Superior Computing Heart for preliminary picture processing: Stampede2 was used to take away background noise and artifacts, and Frontera, the world’s strongest supercomputer at a US college, was used to sew the photographs collectively to kind a single mosaic. .
“The high-performance computing energy made it attainable to mix myriad photographs and hold the photographs in reminiscence on the similar time for processing, leading to a single lovely picture,” Finkelstein mentioned.
The opposite picture was taken with the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). In comparison with NIRcam, MIRI has a smaller discipline of view however operates at a a lot larger spatial decision than earlier mid-infrared telescopes. MIRI detects longer wavelengths than NIRCam, permitting astronomers to see cosmic mud shining from star-forming galaxies and black holes at modestly giant distances, and to see mild from older stars at very nice distances.
The file for essentially the most distant galaxy has simply been damaged once more, 250 million years after the Large Bang
Steven L. Finkelstein et al, A Lengthy Time In the past in a Galaxy Far, Far Away: A Candidate z~14 Galaxy in Early JWST CEERS Imaging, arXiv (2022). arXiv:2207.12474 [astro-ph.GA]arxiv.org/abs/2207.12474
arXiv
Supplied by the College of Texas at Austin
Quote: Vast view of the universe’s earliest clues to the galaxy among the many oldest ever detected (2022, August 4) Retrieved August 4, 2022 from https://phys.org/information/2022-08-wide-view-early -universe-hints.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from honest use for functions of personal examine or analysis, no half could also be reproduced with out written permission. The content material is offered for info solely.
#Vast #view #universes #clues #galaxy #amongst #oldest #detected
